
MRO MARCI Weather Report for the week of
|
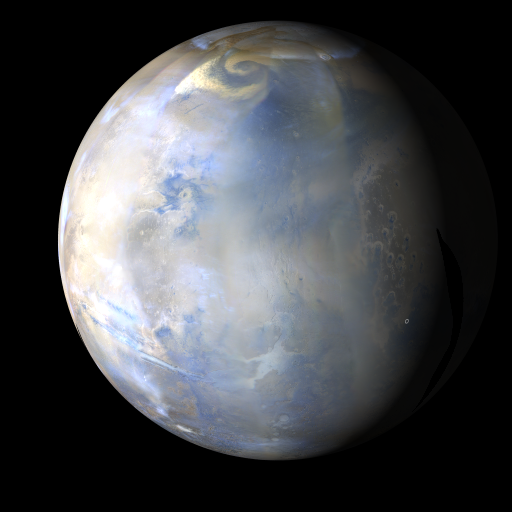 CLICK to play Quicktime Movie (9 MB) NASA/JPL/Malin Space Science Systems |
Martian Weather Between 25 February 2008 to 2 March 2008:
The MARCI acquires a global view of the red planet and its weather patterns every day. Please click and play the Quicktime movie (.mov file) to see how the weather on Mars changed during this time.
There was increased dust storm activity at mid-latitudes in both hemispheres this past week. The most notable dust storms were observed in northern Tempe near the seasonal north polar cap edge. The largest of these storms developed during the latter half of the week, becoming almost regional in areal extent. The storm developed a well-defined spiral (counter-clockwise) shape, similar in morphology to a terrestrial low-pressure (cold) front. Dust lofted by the storm was transported as far north as the perennial north polar water ice cap. As for water ice clouds, they continued to be observed over the large volcanoes (Tharsis Montes, Olympus Mons, and Elysium Mons), near the seasonal north polar cap edge, and at southern mid-latitudes.
Earlier Mars Weather Reports are available HERE.
About the Quicktime Movie:
The movie (a .mov file that you can click and play, above)
was generated from images obtained by the Mars Color Imager (MARCI) onboard the
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). During a nominal operational week, a total
of about 273 MARCI images, taken in three of the camera’s seven color filter
bands (420, 550, and 600 nanometer wavelengths), are map projected and mosaiced together to produce seven false-color daily
global maps. These maps are then projected onto a sphere with north at the top and east to the right and
with the mid-afternoon vantage point of an observer in the orbital plane (the imaginary plane that the planet
draws out as it circles the Sun).
Black areas in the movie are the result of data drops or high angle roll maneuvers by the spacecraft that limit
the camera’s view of the planet. Equally-spaced blurry areas that run from south-to-north (bottom-to-top) result
from the high off-nadir viewing geometry, a product of the spacecraft’s low-orbit, 250 km x 316 km (155 miles x 196 miles).
The movie is rendered at a lower resolution than the intrinsic 1–2 km nadir resolution that the MARCI provides, so that it
is practical to view and share via the Internet. The small white circles on these images of Mars indicate the
locations of the two Mars Exploration Rovers, Opportunity (on Meridiani Planum) and Spirit (in Gusev Crater). Other locations
on Mars referenced in the weather report can be found by referring to the map below. Note that the still image of Mars depicted
at the top of this page is a single frame from the Quicktime movie.
|
Reference Map — Martian Place Names Commonly Mentioned in Mars Weather Reports
NASA/JPL/Malin Space Science Systems |
Citation and Credit
The image(s) and caption are value-added products. MSSS personnel processed the images
and wrote the caption information. While the image(s) are in the Public Domain,
NASA/JPL/MSSS requests that you credit the source of the image(s). Re-use of the
caption text without credit is plagiarism.
Please give the proper credit for use of the image(s) and/or caption.
Image Credit:
NASA/JPL/Malin Space Science Systems
—or—
NASA/JPL/MSSS
To cite the image(s) and caption information in a paper or report:
Malin, M. C., B. A. Cantor, D. E. Shean, M. R. Kennedy and J. A. Lougen (2008), MRO MARCI Weather Report for the week of 25 February 2008 – 2 March 2008, Malin Space Science Systems Captioned Image Release, MSSS-20,
http://www.msss.com/msss_images/2008/03/05/.
Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) built and operates the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Mars Color Imager (MARCI) and Context Camera (CTX). MSSS also built and operated the Mars Global Surveyor (MGS) Mars Orbiter Camera (MOC). In addition, MSSS built the Mars Odyssey (ODY) Thermal Emission Imaging Spectrometer (THEMIS) Visible (VIS) camera subsystem, which shares optics with the thermal infrared instrument and is operated at Arizona State University (ASU). MSSS built the Mars Descent Imager (MARDI) for the Phoenix Mars Scout lander and in 2008 is designing a camera for the 2011 Juno Mission to Jupiter and is completing camera systems for the 2009 Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover mission and the 2008 Lunar Reconnassaince Orbiter (LRO).
 Malin Space Science Systems, Inc., San Diego, California, U.S.A.
Malin Space Science Systems, Inc., San Diego, California, U.S.A.